Ultra High-Performance Database OpenM(ysq)LDB: Seamless Compatibility with MySQL Protocol and Multi-Language MySQL Client
Contents
Ultra High-Performance Database OpenM(ysq)LDB: Seamless Compatibility with MySQL Protocol and Multi-Language MySQL Client#
What’s OpenM(ysq)LDB?#
OpenMLDB has introduced a new service module called OpenM(ysq)LDB, expanding its capabilities to integrate with MySQL infrastructure. This extension redefines the “ML” in OpenMLDB to signify both Machine Learning and MySQL compatibility. Through OpenM(ysq)LDB, users gain the ability to utilize MySQL command-line clients or MySQL SDKs in various programming languages, enabling seamless access to OpenMLDB’s unique online and offline feature calculation capabilities.
OpenMLDB itself is a distributed high-performance memory time-series database built on C++ and LLVM technologies. Its architectural design and implementation logic significantly differ from traditional standalone relational databases like MySQL. OpenMLDB has garnered widespread adoption, particularly in hard real-time online feature calculation scenarios such as financial risk control and recommendation systems. While OpenMLDB’s capabilities are robust, its adoption was initially hindered by perceived high adaptation costs.
However, the introduction of OpenM(ysq)LDB addresses this barrier by facilitating direct integration with MySQL Clients and SDKs. Through standard ANSI SQL interfaces, OpenMLDB is now compatible with MySQL protocol, allowing customers to directly use the familiar MySQL clients to access OpenMLDB data and perform special OpenMLDB SQL feature extraction syntax. This enhancement streamlines the transition for users familiar with MySQL environments, making OpenMLDB’s advanced features more accessible and user-friendly.
For more details, check the official documentation.
Usage#
Use a Compatible MySQL Command Line#
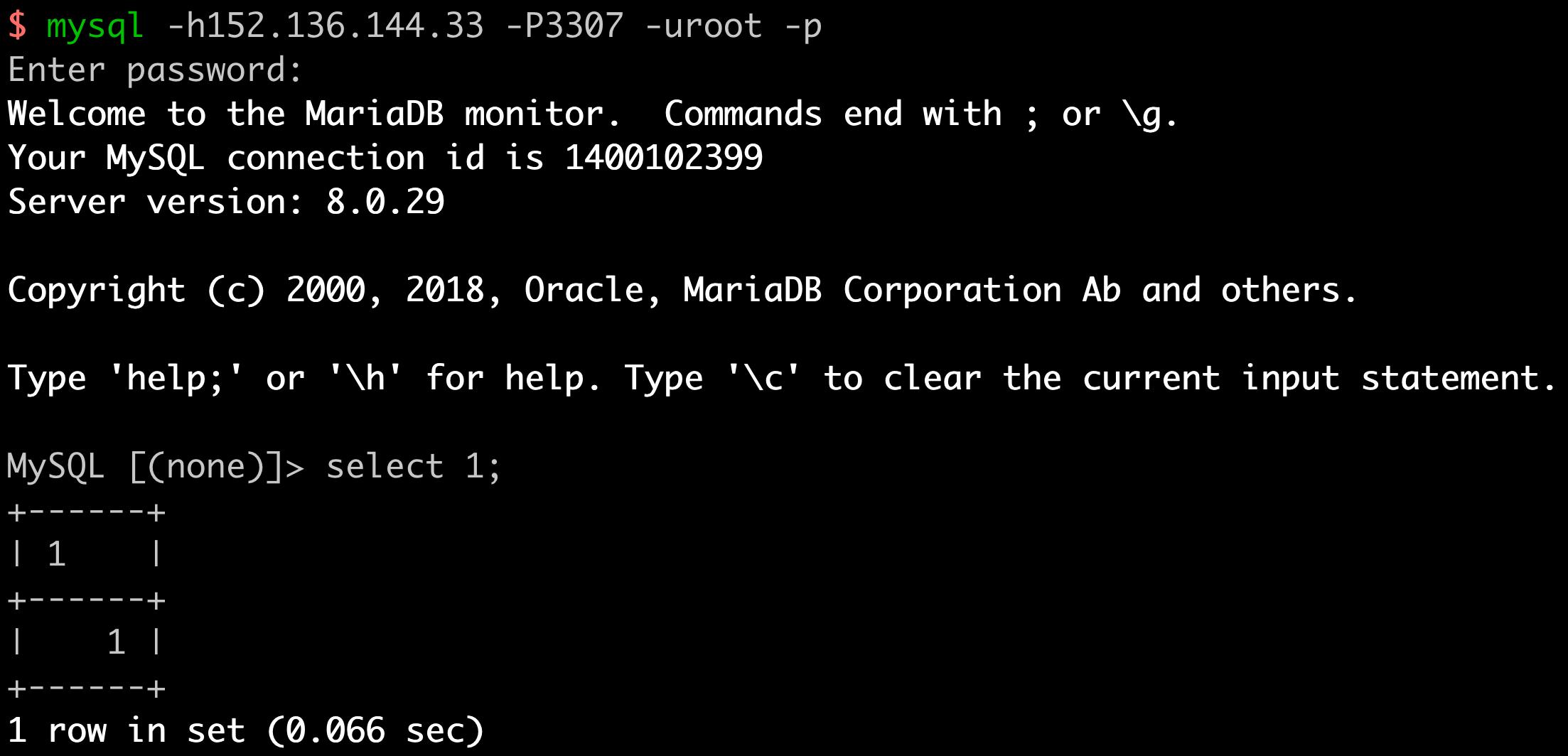
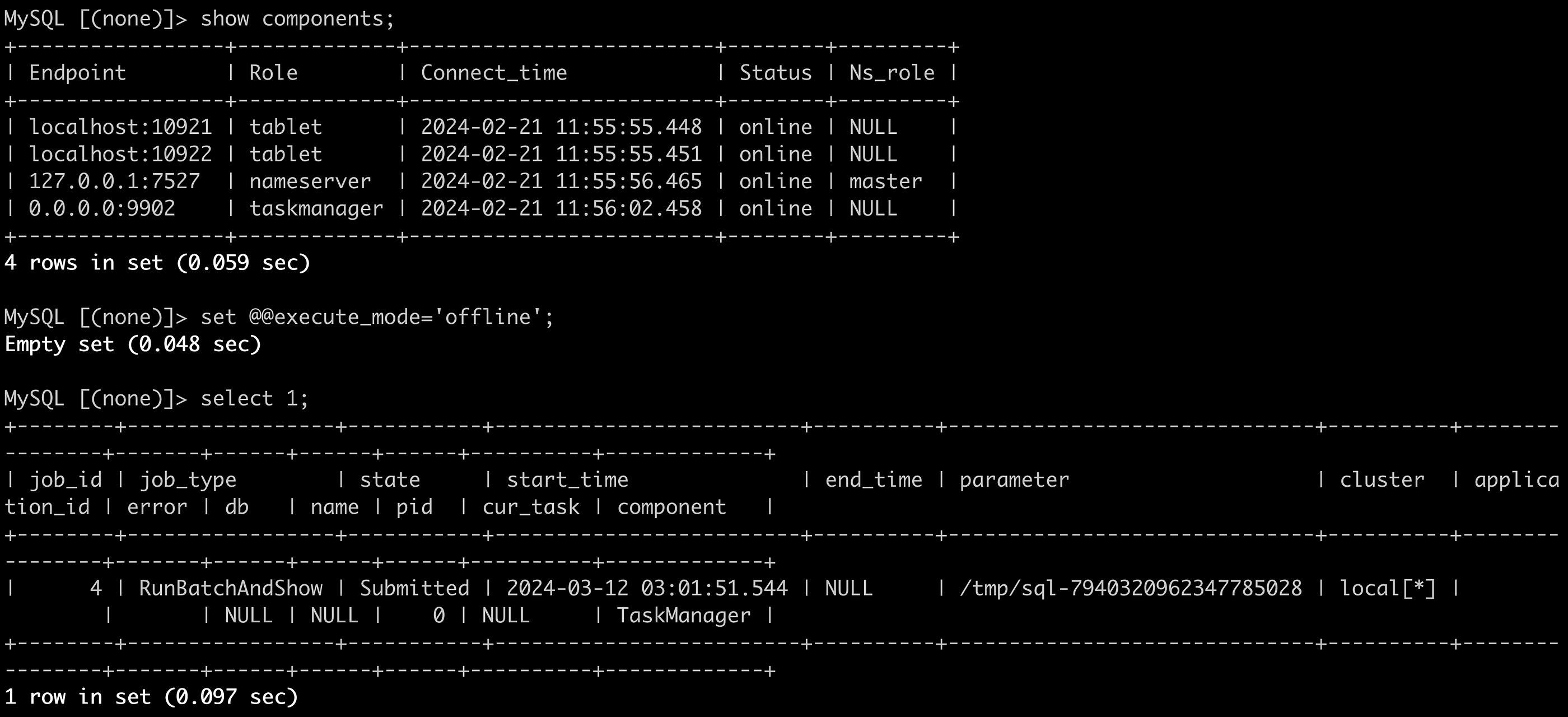
After deploying the OpenMLDB distributed cluster, developers do not need to install additional OpenMLDB command line tools. Using the pre-installed MySQL command line tool, developers can directly connect to the OpenMLDB cluster for testing ( note that the following SQL connections and execution results are all returned by the OpenMLDB cluster, not by a remote MySQL service).
By executing customized OpenMLDB SQL, developers can not only view the status of the OpenMLDB cluster but also switch between offline mode and online mode to realize the offline and online feature extraction functions of MLOps.
Use a Compatible JDBC Driver#
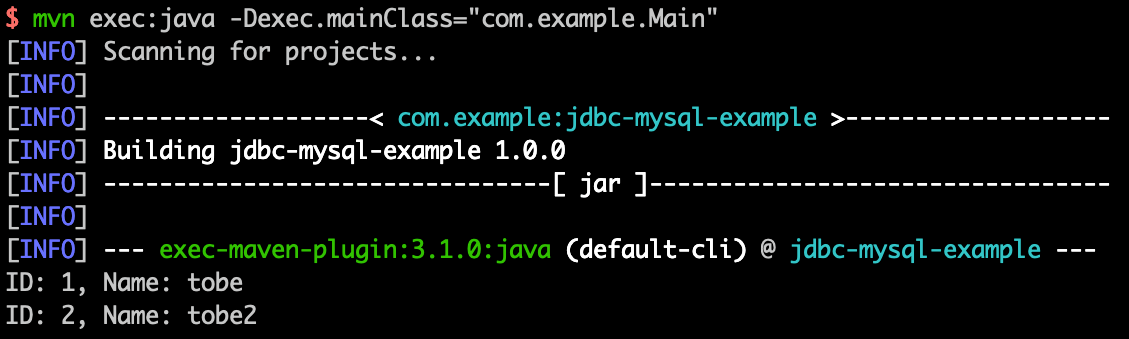
Java developers generally use the MySQL JDBC driver to connect to MySQL. The same code can directly connect to the OpenMLDB cluster without any modification.
Write the Java application code as follows. Pay attention to modifying the IP, port, username, and password information according to the actual cluster situation.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3307/db1";
String user = "root";
String password = "root";
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
statement = connection.createStatement();
resultSet = statement.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM db1.t1");
while (resultSet.next()) {
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
System.out.println("ID: " + id + ", Name: " + name);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// Close the result set, statement, and connection
try {
if (resultSet != null) {
resultSet.close();
}
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
Then compile and execute, and you can see the queried data for the OpenMLDB database in the command line output.
Use a Compatible SQLAlchemy Driver#
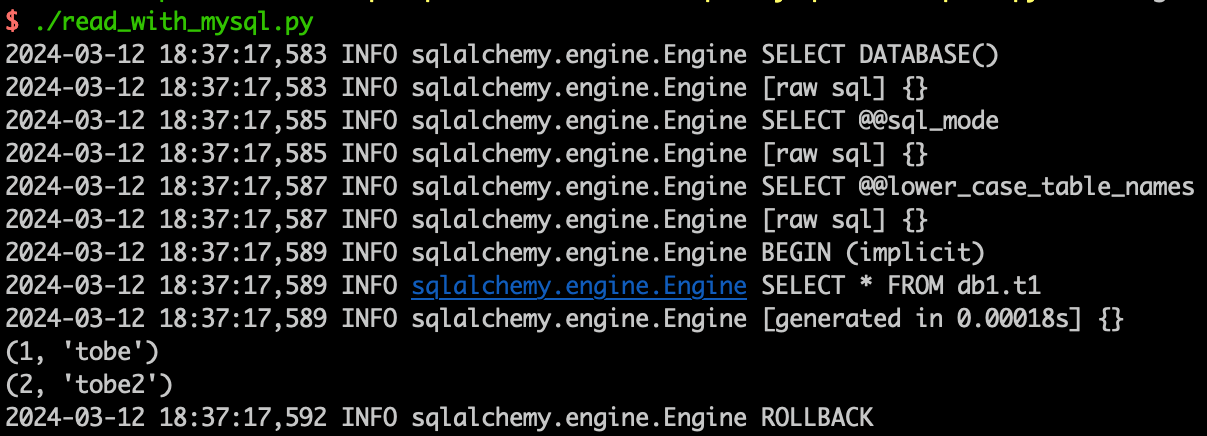
Python developers often use SQLAlchemy and MySQL drivers, and the same code can also be directly applied to query OpenMLDB’s online data.
Write the Python application code as follows:
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, text
def main():
engine = create_engine("mysql+pymysql://root:root@127.0.0.1:3307/db1", echo=True)
with engine.connect() as conn:
result = conn.execute(text("SELECT * FROM db1.t1"))
for row in result:
print(row)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Then execute it directly, and you can see the corresponding OpenMLDB database output in the command line output.
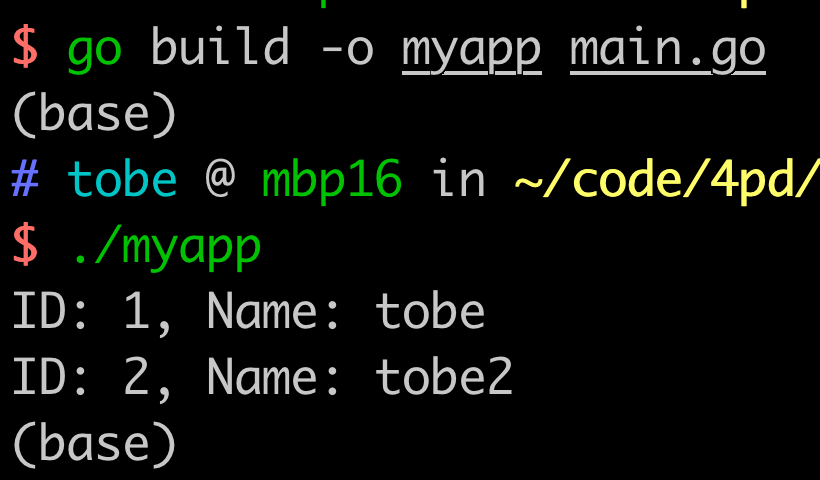
Use a Compatible Go MySQL Driver#
Golang developers generally use the officially recommended github.com/go-sql-driver/mysql driver to access MySQL. They can also directly access the OpenMLDB cluster without modifying the application code.
Write the Golang application code as follows:
package main
import (
"database/sql"
"fmt"
"log"
_ "github.com/go-sql-driver/mysql"
)
func main() {
// MySQL database connection parameters
dbUser := "root" // Replace with your MySQL username
dbPass := "root" // Replace with your MySQL password
dbName := "db1" // Replace with your MySQL database name
dbHost := "localhost:3307" // Replace with your MySQL host address
dbCharset := "utf8mb4" // Replace with your MySQL charset
// Create a database connection
db, err := sql.Open("mysql", fmt.Sprintf("%s:%s@tcp(%s)/%s?charset=%s", dbUser, dbPass, dbHost, dbName, dbCharset))
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Error connecting to the database: %v", err)
}
defer db.Close()
// Perform a simple query
rows, err := db.Query("SELECT id, name FROM db1.t1")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Error executing query: %v", err)
}
defer rows.Close()
// Iterate over the result set
for rows.Next() {
var id int
var name string
if err := rows.Scan(&id, &name); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Error scanning row: %v", err)
}
fmt.Printf("ID: %d, Name: %s\n", id, name)
}
if err := rows.Err(); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Error iterating over result set: %v", err)
}
}
Compile and run directly, and you can view the database output results in the command line output.
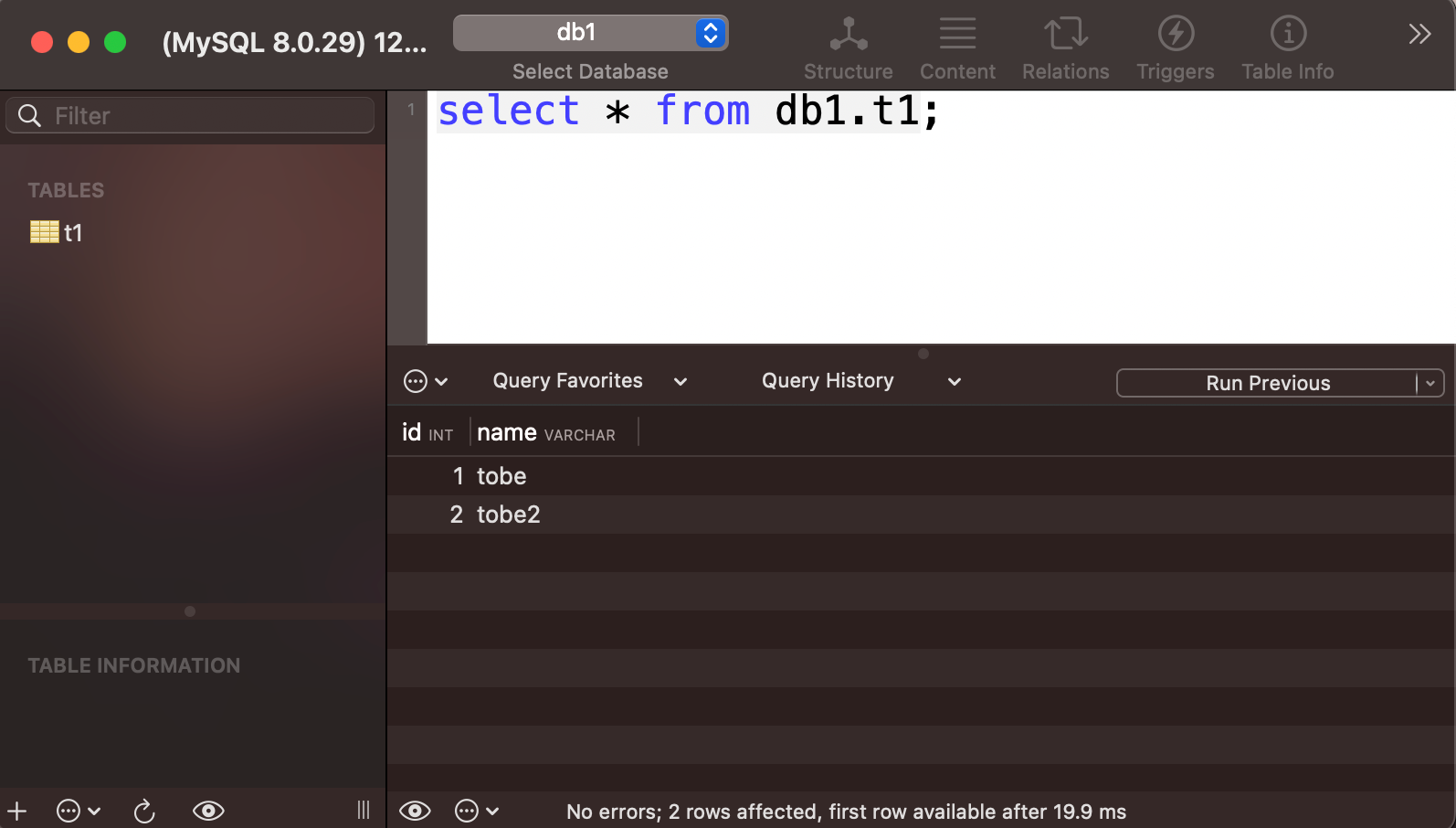
Use a Compatible Sequel Ace Client#
MySQL developers usually use GUI applications to simplify database management. If developers want to connect to an OpenMLDB cluster, they can also use such open-source GUI tools.
Taking Sequel Ace as an example, developers do not need to modify any project code. They only need to fill in the address and port of the OpenM(ysq)LDB service when connecting to the database and fill in the username and password of the OpenMLDB service as the username and password. Then developers can follow the MySQL operation method to access the OpenMLDB service.
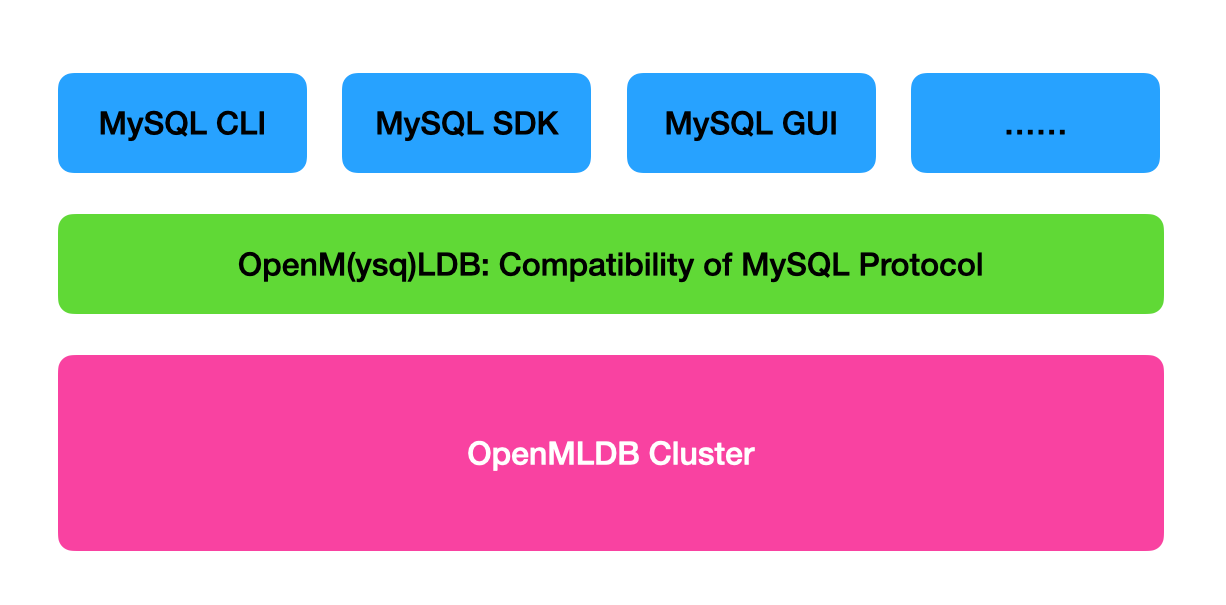
Compatibility Principle of MySQL Protocol#
The protocols of MySQL (including subsequent versions like MariaDB) are publicly available. On the server side, OpenM(ysq)LDB fully implements and is compatible with the MySQL protocol. While at the backend, it manages connections to the distributed OpenMLDB cluster through the OpenMLDB SDK, enabling compatibility access with various MySQL clients.
Currently, OpenM(ysql)LDB maintains client interaction with OpenMLDB through long-lived connections. This ensures that each connection has a unique client object accessing the OpenMLDB cluster. All SQL queries from the same connection do not require additional initialization, and resources are automatically released after the connection is closed. The overhead of the service itself is almost negligible, and performance can be consistent with directly connecting to OpenMLDB.
For more usage documentation, please refer to the official documentation.
Summary#
OpenM(ysql)LDB is a bold attempt within the OpenMLDB project. After a total of 39 versions released from 0.1.5 to 0.8.5, and continuous improvement in functionality and SQL syntax compatibility, it has finally achieved full compatibility with the MySQL protocol. It not only ensures basic SQL query functionality but also provides a lower-level storage implementation and AI capabilities that outperform MySQL. From now on, MySQL/MariaDB users can seamlessly switch their database storage engines. Developers using different programming languages can also directly utilize mature MySQL SDKs. The barrier to entry for using OpenMLDB services has been significantly lowered, providing a “shortcut” for all DBAs or data developers to transition to AI.
Please note that as of now, MySQL Workbench testing with OpenM(ysql)LDB is not yet supported. Relevant testing work is still ongoing, and interested developers can stay updated on the development progress of this project on GitHub.
For more information on OpenMLDB:
Official website: https://openmldb.ai/
Documentation: https://openmldb.ai/docs/en/
Join us on Slack!
This post is a re-post from OpenMLDB Blogs.